Penetration Test Method – Standard Split Spoon Sampler
The equipment used for this test may be a standard split spoon sampler, a cone or other specially shaped tool. The test consists of measuring the resistance offered by the soil to the penetration of the test-tool under dynamic or static loading. The values of resistance, also known as N values, are co-related with properties of soil, such as density, bearing capacity etc. Thus, based on information about N values, it is possible to determine the bearing capacity of soil by use of standard graphs or tables. In this split spoon sampler method, a hole 55 to 150 mm in diameter is made in the ground with the help of suitable equipment for conducting the test. It may sometimes be necessary to use casing or drilling mud where the soil at site is sandy, soft clay or other such type where the sides of the hole are likely to cave in. At sites where casing is used to keep the walls of the test hole stable, it should not be driven below the level at which the test is to be made or soil sample is to be taken. The distance between end of casing and bottom of bore hole should not be more than 150 mm.The casing should preferably be sunk in ground by turning it slowly instead of driving it so as to ensure that it does not disturb the soil and hence the test is performed on undisturbed soil.
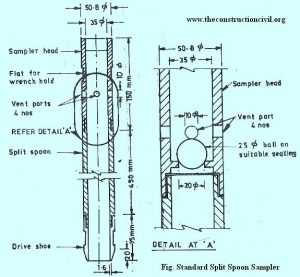
A standard split spoon sampler consists of a thick wall tube having outer diameter of 50.8 mm and internal diameter of 35 mm and a length of 6OO mm. The tube has a drive shoe attached to its bottom and coupling head at top to accommodate the drill rod, used for testing. The drill rod is coupled to sampler head and the sampler is lowered into the clean hole, made in the ground in advance. The sampler is driven into the undisturbed soil at the bottom of the hole, with the help of a driving weight assembly consisting of a driving head and a 650 N weight with 750 mm free fall. The blows from the driving weight fall on the drill rod which drives the sampler into the soil. The sampler is first driven through 150 mm in the hole. This is known as seating drive. The sampler is then driven further through 300 mm and the number of blows required for 300mm penetration are recorded. This number of blows is termed as penetration resistance of soil and is represented by symbol N.
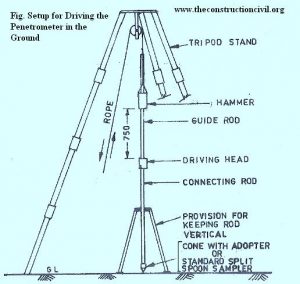
The tests are made and samples are taken out at every change in stratum or at intervals of 15 m whichever is less.
In case of very fine or silty saturated sand, it is seen that although they have less value of bearing capacity, yet, due to apparent increase in resistance that such type of soil offer to penetration of the sampler, the N values obtained by this test are more and as such Terzaghi and Peck recommend adoption of an equivalent penetration resistance (Ns) in place of actually observed value of N, where N is greater than 15.
Ns is given by formula,
Ns = 15 + 0.5(N-15)
